Yoga Blog
Exploring the Profound Impact of Yoga on Your Mental and Emotional Health
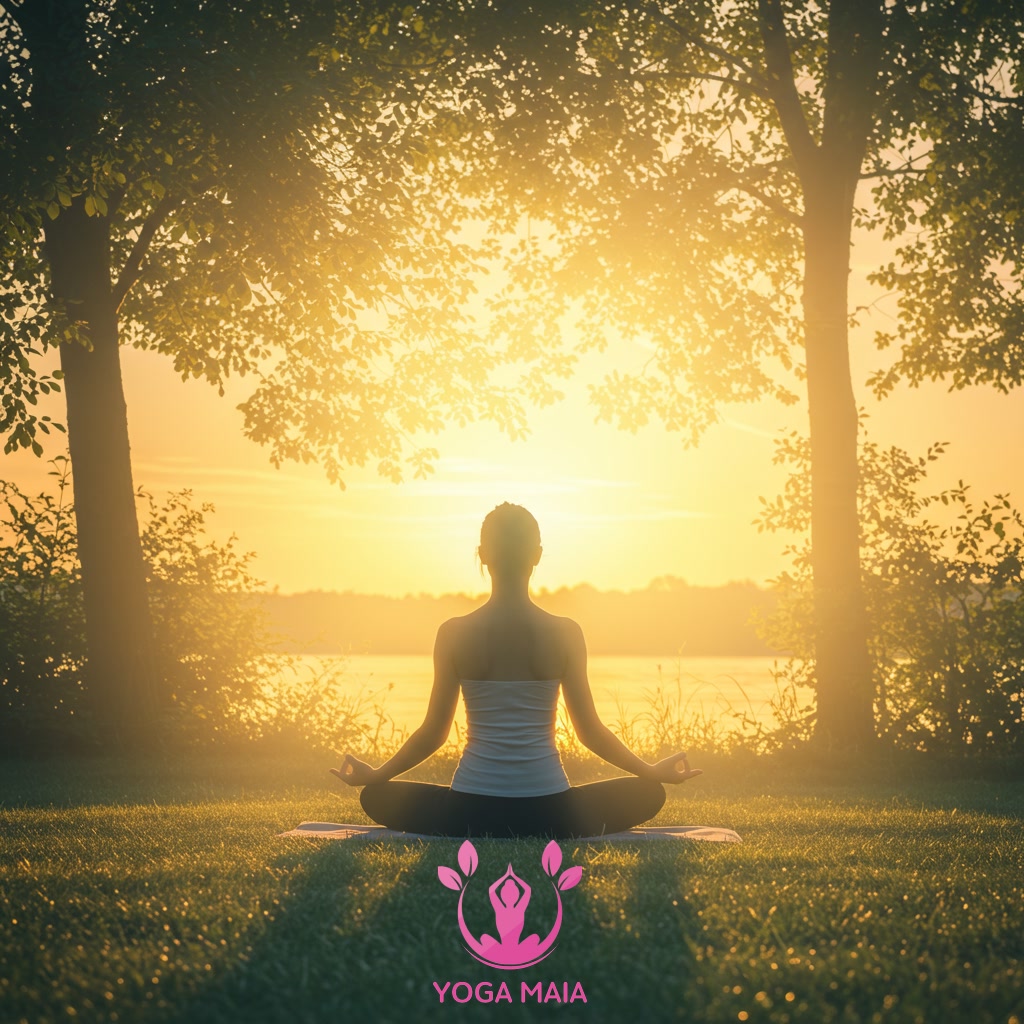

This exploration delves into how the practice of yoga significantly influences mental and emotional health. It examines the various ways yoga techniques can help reduce stress, manage anxiety, and improve mood. The content highlights yoga’s role in fostering greater self-awareness and emotional resilience. Ultimately, it illustrates the transformative power of yoga on one’s overall well-being.
Table of Contents
- Section 1: Understanding the Mind-Body Connection and Yoga
- Section 2: Physiological Mechanisms: How Yoga Affects Your Brain and Nervous System
- Section 3: Yoga as a Powerful Tool for Reducing Stress and Anxiety
- Section 4: Cultivating Emotional Balance and Resilience Through Yoga Practice
- Section 5: Integrating Yoga into Your Life for Lasting Mental and Emotional Well-being
Section 1: Understanding the Mind-Body Connection and Yoga
The core principle of yoga lies in recognizing and strengthening the intrinsic link between our mental state and physical being – the mind-body connection. This connection isn’t merely theoretical; it’s experienced directly on the mat. Through physical postures (asanas), we cultivate awareness of bodily sensations and movements. Simultaneously, conscious breathing techniques (pranayama) serve as a bridge, calming the nervous system and focusing the mind. This deliberate practice helps us observe how physical tension relates to mental stress or how a relaxed body can foster a peaceful mind. By consciously engaging both the body and breath, yoga teaches us to navigate our emotional landscape by understanding its physical manifestations, fostering a deeper, integrated sense of self and well-being.
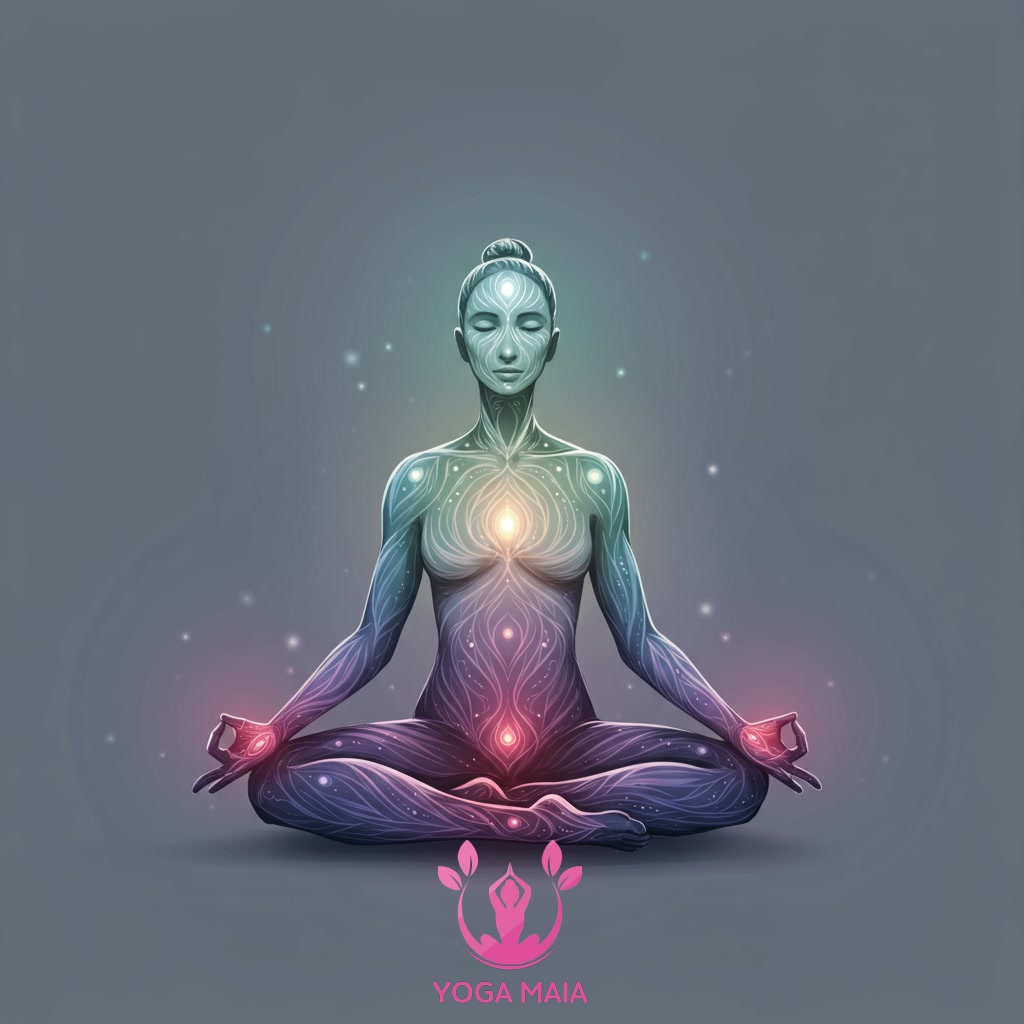 Understanding the Mind-Body Connection and Yoga
Understanding the Mind-Body Connection and Yoga
Section 2: Physiological Mechanisms: How Yoga Affects Your Brain and Nervous System
Building on the recognition of the mind-body connection, yoga profoundly impacts our physiology, particularly the brain and nervous system. Through practices like controlled breathing (pranayama) and physical postures (asana), yoga helps regulate the autonomic nervous system, shifting it from the ‘fight or flight’ sympathetic mode towards the calming ‘rest and digest’ parasympathetic mode. This shift reduces stress hormones like cortisol. Regular yoga practice has also been shown to influence brain structures, potentially increasing gray matter in areas associated with self-awareness and emotional regulation, such as the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus, while potentially reducing the size and activity of the amygdala, the brain’s fear center. Furthermore, the mindful movement and breathing can promote the release of neurotransmitters like GABA, which has a calming effect, contributing to reduced anxiety and improved mood.
 Physiological Mechanisms: How Yoga Affects Your Brain and Nervous System
Physiological Mechanisms: How Yoga Affects Your Brain and Nervous System
Section 3: Yoga as a Powerful Tool for Reducing Stress and Anxiety
Building on the connection between the mind and body, yoga acts as a profound intervention for the stress and anxiety response, directly impacting the nervous system. Techniques such as controlled diaphragmatic breathing (pranayama) activate the parasympathetic nervous system, often referred to as the “rest and digest” mode, counteracting the “fight or flight” response triggered by stress. Holding physical postures (asanas) releases physical tension stored in the body, which is often a manifestation of psychological stress. The meditative aspect inherent in yoga practice, focusing on present moment awareness, helps to quiet the incessant stream of anxious thoughts. This combination of physical movement, breath regulation, and mindfulness effectively lowers cortisol levels, the primary stress hormone, leading to a tangible reduction in feelings of stress and anxiety and promoting a state of calm.
 Yoga as a Powerful Tool for Reducing Stress and Anxiety
Yoga as a Powerful Tool for Reducing Stress and Anxiety
Section 4: Cultivating Emotional Balance and Resilience Through Yoga Practice
Building on the idea of calming the nervous system, yoga actively supports the cultivation of emotional balance. Through focused breathwork (pranayama) and mindful physical postures (asana), practitioners learn to regulate their physiological responses to stress and challenging emotions. This practice creates a space for observing feelings without immediate reaction or judgment. By consistently engaging with discomfort in a controlled environment on the mat, individuals build tolerance and develop the capacity to remain present and centered amidst life’s inevitable ups and downs. This enhanced self-awareness and non-reactivity are fundamental to building emotional resilience, enabling a more stable and adaptive response to emotional challenges.
 Cultivating Emotional Balance and Resilience Through Yoga Practice
Cultivating Emotional Balance and Resilience Through Yoga Practice
Section 5: Integrating Yoga into Your Life for Lasting Mental and Emotional Well-being
Building on the idea of cultivating emotional balance through specific techniques, integrating yoga into your daily routine is key to sustaining these benefits over time. This doesn’t necessarily mean hours on the mat; even short, consistent practices can make a significant difference. Consider starting with a few minutes of mindful breathing in the morning, incorporating a few simple poses during a break, or dedicating a longer session a few times a week. The goal is to make yoga a regular, accessible part of your life, allowing its calming and centering effects to become a consistent support for managing stress, enhancing mood, and building resilience against life’s challenges. Finding a style and schedule that fits your lifestyle is crucial for making this integration successful and fostering long-term mental and emotional well-being.
 Integrating Yoga into Your Life for Lasting Mental and Emotional Well-being
Integrating Yoga into Your Life for Lasting Mental and Emotional Well-being












