Yoga Blog
Discover How Yoga Improves Your Breathing: A Guide to Respiratory Health

This guide explores how incorporating yoga can significantly improve respiratory health. It delves into specific techniques and practices within yoga designed to enhance breathing function and capacity. Discover practical methods to achieve better breath control and overall pulmonary well-being through yoga.
Table of Contents
- Section 1: Introduction: The Vital Role of Breathing in Health
- Section 2: Understanding Pranayama: The Yogic Practice of Breath Control
- Section 3: Key Pranayama Techniques for Enhanced Respiratory Function
- Section 4: Yoga Asanas (Poses) That Support and Open the Chest and Lungs
- Section 5: The Science Behind Yoga’s Impact on Respiratory Health
- Section 6: Beyond Better Breathing: Additional Benefits of Yoga for Well-being
- Section 7: Integrating Yoga and Breathwork into Your Daily Routine
Section 1: Introduction: The Vital Role of Breathing in Health
Breathing is the most fundamental rhythm of life, a constant, often unconscious process that fuels every cell in our body. We breathe approximately 20,000 times a day, yet few of us truly appreciate its profound impact on our physical and mental well-being. Beyond simply supplying oxygen and expelling carbon dioxide, the way we breathe directly influences our energy levels, stress response, mood, and even the function of our immune system. Efficient, conscious breathing supports optimal organ function, improves circulation, and helps regulate the nervous system. Understanding and optimizing this vital function is a crucial step towards enhancing overall health and vitality.
 Introduction: The Vital Role of Breathing in Health
Introduction: The Vital Role of Breathing in Health
Section 2: Understanding Pranayama: The Yogic Practice of Breath Control
Building upon the unconscious rhythm of life, yoga introduces the conscious practice of Pranayama, which translates to ‘extension of life force’ or ‘breath control’. Pranayama is a fundamental pillar of yoga, moving beyond simple breathing to deliberate techniques designed to regulate the breath. These methods involve consciously inhaling, holding, and exhaling in specific patterns and durations. By mastering Pranayama, practitioners aim to cleanse the respiratory system, increase lung capacity, calm the nervous system, and enhance the flow of vital energy throughout the body. It’s a bridge between the physical postures (asana) and meditation, offering a powerful tool to gain control over physiological processes and cultivate inner stillness, directly impacting respiratory health and overall well-being.
 Understanding Pranayama: The Yogic Practice of Breath Control
Understanding Pranayama: The Yogic Practice of Breath Control
Section 3: Key Pranayama Techniques for Enhanced Respiratory Function
Building upon the conscious practice of Pranayama introduced previously, this section explores key techniques specifically designed to enhance respiratory function and control. Techniques like Dirga Pranayama (Three-Part Breath) teach conscious awareness and filling of the lungs from bottom to top, increasing overall capacity. Ujjayi Pranayama (Victorious Breath), with its gentle constriction at the back of the throat, creates an audible sound and helps regulate the breath’s length and flow, promoting calm and focus while strengthening respiratory muscles. Nadi Shodhana (Alternate Nostril Breathing) is another foundational practice aimed at balancing energy channels and improving the efficiency of oxygen intake and carbon dioxide release. Mastering these fundamental Pranayama techniques lays the groundwork for deeper respiratory health and control.
 Key Pranayama Techniques for Enhanced Respiratory Function
Key Pranayama Techniques for Enhanced Respiratory Function
Section 4: Yoga Asanas (Poses) That Support and Open the Chest and Lungs
Building upon the conscious practice of Pranayama introduced previously, this section explores key techniques specifically designed to enhance respiratory function and control. Techniques like Dirga Pranayama (Three-Part Breath) help establish a foundation for fuller breathing. Moving beyond breath-specific exercises, certain yoga asanas, or poses, are invaluable for physically creating space within the chest and rib cage. Poses such as Cobra Pose (Bhujangasana), Fish Pose (Matsyasana), and Bridge Pose (Setu Bandhasana) gently stretch the intercostal muscles between the ribs and encourage the spine to extend, directly supporting the expansion of the lungs. Practicing these poses regularly can help improve lung capacity and make breathing feel easier and less restricted, complementing the breath control learned in Pranayama.
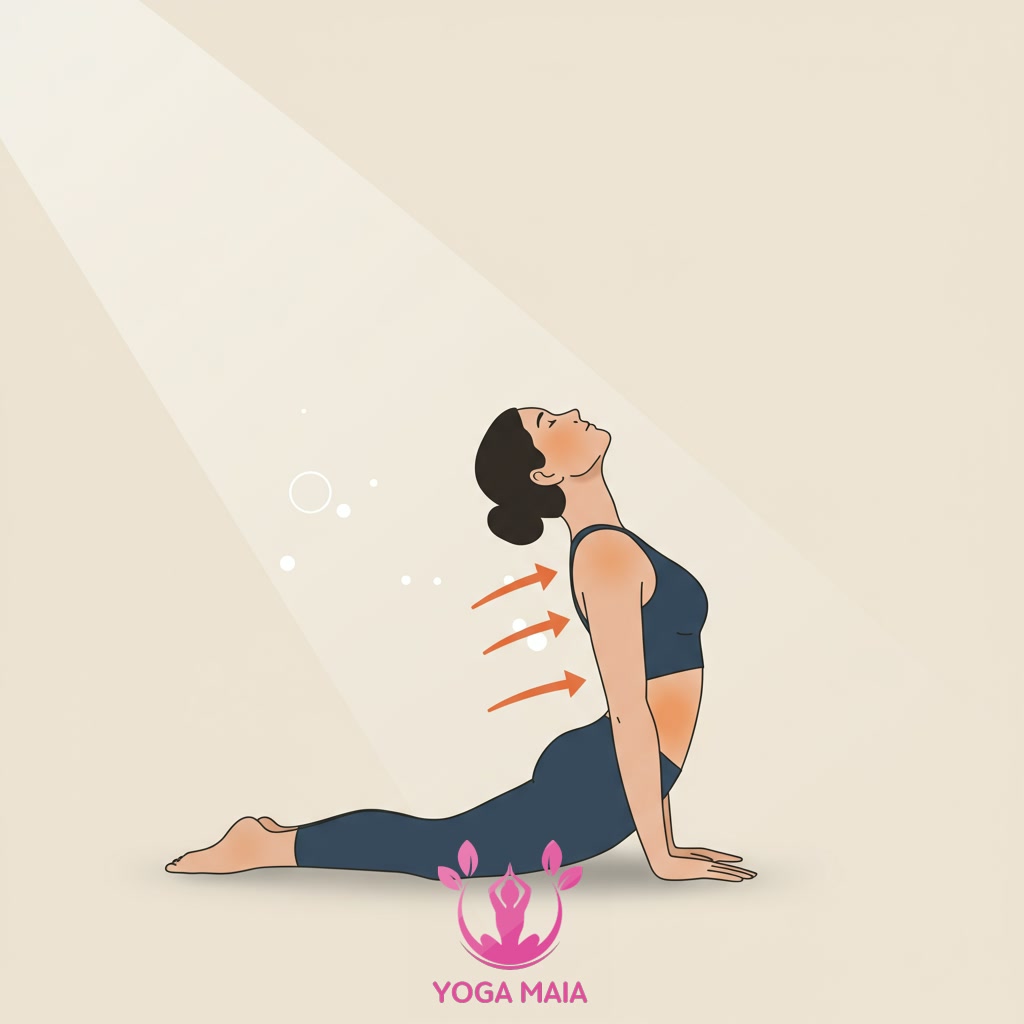 Yoga Asanas (Poses) That Support and Open the Chest and Lungs
Yoga Asanas (Poses) That Support and Open the Chest and Lungs
Section 5: The Science Behind Yoga’s Impact on Respiratory Health
The scientific foundation of yoga’s positive impact on respiratory health lies in its ability to optimize the mechanics and control of breathing. Regular yoga practice, particularly Pranayama techniques, strengthens the diaphragm, the primary muscle of respiration, leading to deeper and more efficient breaths. It also improves the flexibility of the rib cage and spine, allowing for greater lung expansion and increased vital capacity. Furthermore, conscious breathwork influences the autonomic nervous system, shifting dominance towards the parasympathetic branch. This reduces stress-induced shallow breathing and promotes a calmer, more rhythmic respiratory pattern. This physiological shift enhances oxygen uptake and carbon dioxide release, improving overall pulmonary function and promoting a sense of calm and well-being.
 The Science Behind Yoga’s Impact on Respiratory Health
The Science Behind Yoga’s Impact on Respiratory Health
Section 6: Beyond Better Breathing: Additional Benefits of Yoga for Well-being
While the profound impact of yoga on respiratory mechanics and breathing control is well-documented, its benefits extend far beyond pulmonary function alone, significantly contributing to overall well-being. Regular practice fosters a reduction in stress and anxiety through mindfulness and calming poses, which in turn can alleviate tension that might restrict breathing. Improved flexibility and strength developed through various asanas support better posture, further optimizing lung capacity and ease of breath. The mental focus required in yoga cultivates clarity and presence, reducing mental clutter and promoting a sense of calm. Collectively, these physical and mental enhancements create a positive feedback loop, where a healthier body and calmer mind mutually support improved respiratory health and a greater sense of vitality.
 Beyond Better Breathing: Additional Benefits of Yoga for Well-being
Beyond Better Breathing: Additional Benefits of Yoga for Well-being
Section 7: Integrating Yoga and Breathwork into Your Daily Routine
Integrating yoga and breathwork seamlessly into your daily life is key to unlocking their full potential for respiratory health and overall well-being. Start small; even five to ten minutes a day can make a significant difference. Consider incorporating a few simple poses (asanas) paired with conscious breathing exercises (pranayama) first thing in the morning to energize, during a mid-day break to de-stress, or in the evening to wind down. Consistency is more important than duration. Try linking your practice to an existing habit, like before your morning coffee or after brushing your teeth. Finding a dedicated quiet space, even a small corner, can also help establish a routine. This gradual integration makes the practice sustainable and allows you to experience its cumulative benefits over time.
 Integrating Yoga and Breathwork into Your Daily Routine
Integrating Yoga and Breathwork into Your Daily Routine












